
| Home | Documents | Template Program | Citation | |||
 | |||
 Method: i-GSEAThe i-GSEA4GWAS web server implements i-GSEA (improved gene set enrichment analysis) to help researchers explore GWAS data efficiently. i-GSEA is an implementation and extension of the original GSEA for GWAS. The key steps of i-GSEA are the same as GSEA with two highlights: 1) i-GSEA implements SNP label permutation instead of phenotype label permutation to adapt GWAS SNP P-values and to correct gene and gene set variation; 2) i-GSEA multiplies a significance proportion ratio factor to the ES to get the significant proportion based enrichment score (SPES) as described in details below. Briefly, firstly following the classical GSEA for gene expression study [1] and GSEA for GWAS [2], the maximum -log(P-value) or statistics of all the SNPs mapped to a gene was used to represent the gene (t). Then for N genes presented in GWAS, we ranked the genes by decreasing t(1) , t(2) ,¡, t(i) ,..., t(N). For each given gene set S with set size Ns, the enrichment score, ES(S), with parameter w = 1 is calculated: 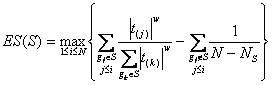 (1) (1)ES(S) emphasizes on the added-up significance of the top genes in S. high ES(S) indicates the association signal in S is highly concentrated at the top of the ranked gene list. Then the key step is: a significant cutoff t0 for the genes mapped with at least one of the top 5% of all SNPs is considered. Instead of ES(S), a significance proportion based enrichment score, SPES(S), is expressed as: 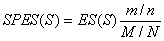 (2) (2)Where m is the number of genes in gene set S, n is the number of all genes in gene set S; M is the number of genes with t > t0 in the GWAS and N is the number of all the genes in the GWAS. SPES emphasizes on the proportion of significant genes in gene set S to avoid the high scoring caused by very few genes with extremely high significance. The following steps, variant label permutation, normalization, calculating gene set P value and FDR, are the same as the classical GSEA for GWAS [2]. As an application, we performed i-GSEA on the P-value data of the GWAS for host control of HIV-1 [3], which has a follow-up study containing the replication of top SNPs and a classical GSEA analysis with phenotype label permutation [4] .By searching database of canonical pathways, i-GSEA identified 5 pathways, three of which were confirmed by our publication [4], and two of which have references to support [5-7]; while by using the classical GSEA, only two pathways were obtained, two of which was confirmed by our publication. By searching database of canonical pathways + GO terms, i-GSEA identified 4 pathways/GO terms and no findings from classical GSEA. This result shows that i-GSEA has the improved sensitivity (Table 1). Table 1 The significant pathways / GO terms (FDR < 0.05) obtained respectively by GSEA and i-GSEA. 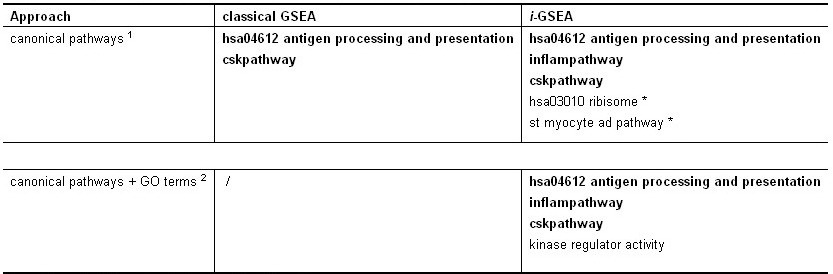
The pathways/GO terms in dark are confirmed by [4].
References |
|
Copyright: Bioinformatics Lab, Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Feedback Last update: June 23, 2010 |